Sustainable technology: data logger with energy harvesting
The omnipresent role of technology extends to all areas of life and plays a central role in industry in particular. However, the use of technology always goes hand in hand with the use of resources and has a significant influence on the shaping of our environment. Against this background, sustainable behaviour and environmental protection are rightly becoming increasingly important. As an innovative company, SenseING also contributes to the development of responsible and sustainable products.
What is sustainable technology?
Sustainable technology is an innovative approach to the development and use of technological solutions that aims to minimise the impact on the environment and promote social responsibility. This approach is reflected at various levels, which can have a positive impact in equally diverse areas.
Renewable energies, for example, are a central aspect of sustainable technologies and include the utilisation of environmentally friendly energy sources such as sun, wind, water and geothermal energy. This form of energy generation reduces dependence on non-renewable resources and at the same time reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
The efficient use of energy and resources also plays a crucial role. Technologies to improve energy efficiency in buildings, means of transport and industrial processes help to minimise consumption and thus reduce environmental pollution.
Recycling is another level of sustainable technology. By developing advanced recycling processes and increasing the recyclability of products, resources can be reused more efficiently, reducing not only the amount of waste but also the need for primary raw materials.

Digital technologies also contribute to sustainability by offering innovative solutions for environmentally friendly processes, intelligent urban development and environmentally conscious data collection.
All in all, sustainable technology is a multi-layered approach that works at various levels to promote environmentally friendly, socially responsible and sustainable development.
How SenseING designs sustainable products
Disposable data loggers are frequently used in the transport sector in particular. Although these are practical, their short-term benefits are often at the expense of the environment. SenseING has set itself the goal of solving this problem by using reusable loggers. We develop and produce products that are designed for durability and reliability so that our customers can benefit from our solutions for a long time. In doing so, we actively consider the various levels of sustainable technology:
Energy harvesting: energy from the environment
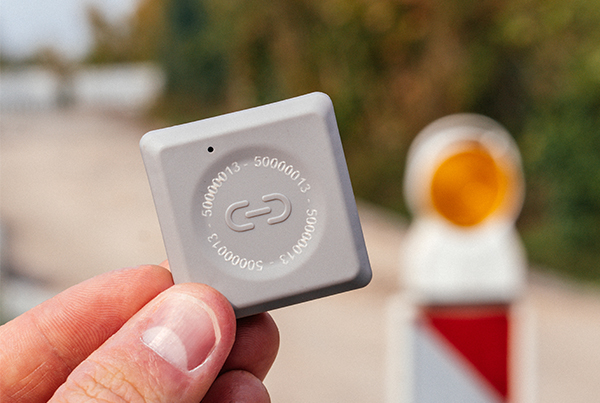
In its products, SenseING SLC-PV and SNC-PV relies on the integration of indoor solar cells, which enable self-sufficient operation of the data loggers. The use of solar energy has not only ecological but also practical advantages. Thanks to the continuous energy supply, our data loggers can supply themselves with energy over very long periods of time. This not only saves the hassle of changing batteries or recharging, but also significantly reduces the total cost of ownership. Thanks to the intelligent utilisation of indoor lighting in buildings, the data loggers can also be operated in environments where no direct sunlight is available. At the same time, the problem of assigning data to objects is solved, as self-sufficient data loggers can be permanently attached to products such as insulated containers. Manual assignment processes, as required with disposable data loggers, are thus completely eliminated.
Ultra-Low Power

Die Energieeffizienz unserer Datenlogger ist ein entscheidender Faktor. Dank unseres innovativen Ultra-Low-Power-Designs haben die Logger einen extrem niedrigen Energieverbrauch. Dies ermöglicht nicht nur den Langzeitbetrieb von batteriebetriebenen Loggern über mehrere Jahre, sondern auch den autarken Betrieb mit Hilfe von Energy Harvesting Modulen – selbst in Umgebungen ohne direktes Tageslicht. Die Fokussierung auf Ultra Low Power eröffnet neue Perspektiven für eine nachhaltige und effiziente Nutzung von Energiequellen in verschiedenen Anwendungsbereichen, insbesondere im IoT area.
Recyclable design
SenseING's sustainable approach is also reflected in the hardware of its products. An integral part of the product design is the consistent focus on recyclability. Our products are designed so that they can be easily recycled at the end of their service life in order to minimise the environmental impact and make optimum use of resources. The modular design also allows components such as the housing to be replaced in the event of damage, so that the centrepiece of the hardware, the electronics, can continue to be used.
If you would like to find out more about how our Data loggers and sensors work or how they are used in your industry ,we are at your disposal. Contact us and discover how sustainable technology is revolutionising the way we collect and analyse data.